Research - OSF Study 1
Work has been completed on a formal confirmatory research study on inductive pulse charging (IPC) after 6 years of exploratory investigation into claims of energy gains in Lead-acid and Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries.
This technology is based on a long history of related systems derived from experimental observations by Daniel Cook and Nikola Tesla in the 1860-1900s (see patents) and repeated, confirmed, and developed through research and further patents by various pioneers over the last 150 or more years.
The study has been conducted transparently using the Open Science Framework (OSF), the flagship research strategy of the Centre for Open Science, about which an overview can be seen here.
The various uploaded documents cover previous exploratory work and two pre-publication papers, explaining the historical and technical background to the topic, and the technical strategy for a follow-up study, as well as documents that were part of the Pre-Registration process with the OSF.
The time-stamped Pre-Registration study design was submitted in late February 2024 and the experimental work was completed at the end of May, at which time full replication information was provided (see osf.io/54qcn). All the methodologies used, the data gathered and the analyses are available in the various components of the publicly viewable OSF project.
A developmental blog, charting some of the technical improvements leading up to the first study, can be seen here. Lab notes made during the study can also be seen here.
A published paper and a summary of the key findings, indicating energy gains that are not explained by conventional theories, are available here.
All findings are made freely available to researchers and developers to use as they see fit. Any specific commercial innovations resulting from this research will be governed by the local IP of the relevant parties.
The second study, investigating the most likely source of the energy gains, has recently been completed and was published in January 2025.
Research planning material:
OSF Pre-Registration Submission
OSF Pre-Registration - Subject background
OSF Pre-Registration - Design Plan
OSF Pre-Registration - Data Sampling Plan
OSF Pre-Registration - Data Analysis Plan
Closed-Loop Measurement Protocol
Pre-publication material:
Measuring Battery Health: Secondary Cell Dynamics and Electrochemistry
Publications:
Pulse-Induced Energy Gains in Electrochemical Systems (JEEE-2024 (Vol 3, Issue 4, 1-15)).
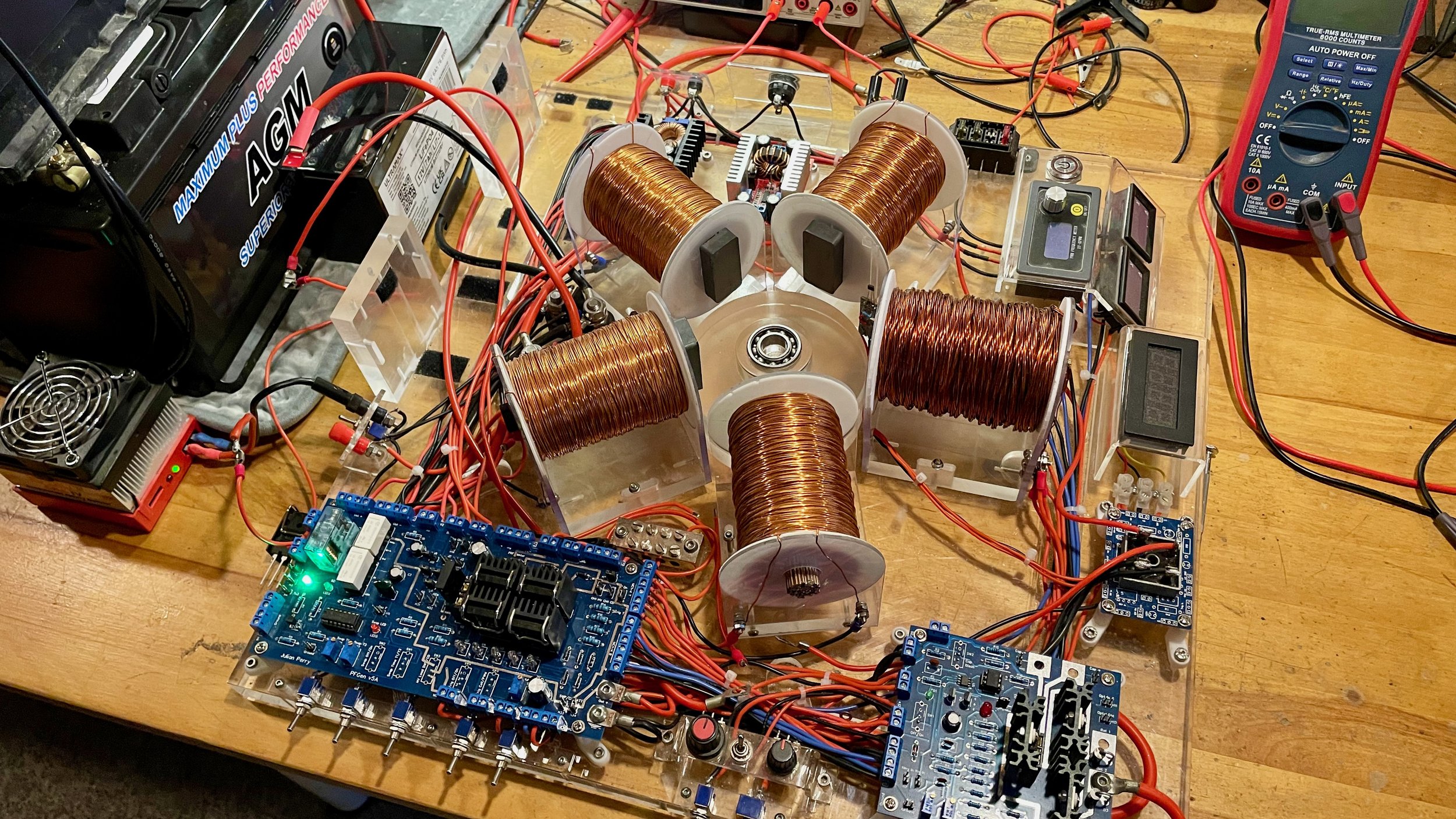
One of various testing setups
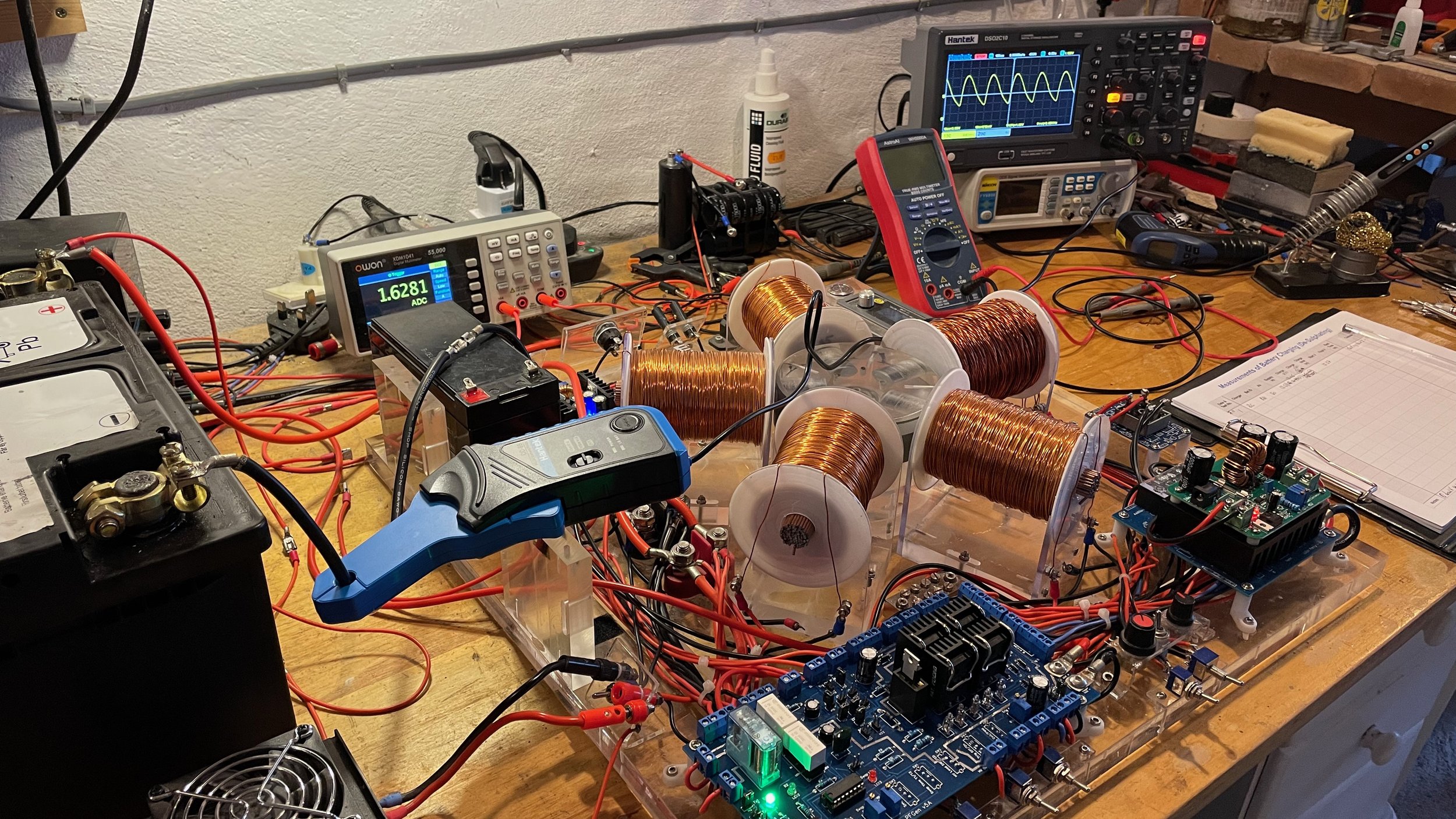
Charging LFP and Pb-Acid AGM batteries using magnetic biasing
Using a current scope meter to observe a charging waveform